Matching nursing interventions to patient needs ensures better care and outcomes. Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Assess Patient Needs: Use tools like Patient Classification Systems (PCS) to evaluate care requirements, focusing on physical, emotional, and social health.
- Create Personalized Care Plans: Involve patients and families, prioritize based on acuity, and use frameworks like the ADPIE process for structured planning.
- Choose Appropriate Interventions: Apply clinical judgment models (e.g., Tanner’s) to select and adjust interventions based on real-time patient conditions.
- Collaborate with Teams: Work with healthcare professionals using clear communication tools like SBAR and document thoroughly.
- Evaluate and Improve: Regularly reassess outcomes, update care plans, and enhance skills through education and evidence-based practices.
This structured approach ensures care is effective, patient-centered, and adaptable to changing needs.
Nursing Care Plan Tutorial
How to Assess Patient Needs
Understanding a patient’s needs is the starting point for providing effective nursing care. This involves a thorough and organized evaluation process that relies on reliable tools and detailed data collection methods.
Using Tools to Measure Patient Acuity
Acuity tools, like Patient Classification Systems (PCS), help structure the evaluation of care needs and guide staffing decisions. These tools rank patients based on how complex and intensive their care requirements are, typically ranging from minimal to maximum care levels.
"A growing body of evidence shows that patient acuity-driven staffing is an effective way to optimize nurse staffing to improve patient outcomes and promote clinical and organizational excellence." [2]
By aligning nurse skills with patient needs, PCS tools enhance care quality, improve staffing efficiency, and lower the risk of negative outcomes.
Collecting Detailed Patient Information
A thorough assessment gathers data about a patient’s physical, emotional, and social health. Key areas to focus on include:
| Assessment Area | Key Focus | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Health | Vital signs, symptoms, medical history | Address urgent medical needs |
| Emotional Status | Mental health, coping strategies | Identify psychological support needs |
| Social Factors | Family support, cultural considerations | Provide well-rounded care |
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) simplify this process by centralizing patient data, enabling real-time updates, and fostering collaboration among care team members.
The AACN Synergy Model [1] emphasizes that accurate assessments are essential for creating care plans that respond to both immediate and changing patient needs. Regular reassessments ensure care remains aligned with these needs, leading to better outcomes. In short, effective care starts with precise, patient-centered assessments.
Armed with this information, the next step is crafting personalized care plans that reflect these insights.
Creating Care Plans for Individual Patients
Developing personalized care plans is key to providing effective patient care after thorough assessments. These plans act as a guide, aligning nursing actions with the specific needs of each patient while staying flexible to accommodate any changes in their condition.
How to Prioritize Care for Multiple Patients
When caring for multiple patients, a structured approach helps ensure that everyone gets the attention they need. Patient acuity classification systems (PCAS) are a useful tool for organizing care, as they rank patients based on the urgency of their needs. This method helps nurses allocate their time and resources effectively.
Here’s a general framework for prioritizing care based on patient acuity:
- High-priority cases: Require immediate attention and frequent monitoring.
- Moderate-priority cases: Need scheduled care and routine evaluations.
- Low-priority cases: Can maintain stability with regular assessments.
Reassessing patients regularly is essential to monitor their progress. Tools like electronic health records (EHRs) make updating care plans more efficient and ensure accurate tracking.
Including Patients and Families in Planning
While prioritizing tasks improves efficiency, involving patients and their families ensures that care aligns with their values and preferences. This collaborative, patient-focused approach often leads to better results and higher satisfaction.
To foster meaningful participation, nurses should:
- Clearly explain the patient’s condition.
- Actively listen to concerns and questions.
- Respect cultural preferences and integrate them into the care plan.
- Document shared goals and agreed-upon interventions.
The AACN Synergy Model [1] emphasizes the importance of matching nurse skills with patient needs to create realistic and effective care plans. This ensures that the planned interventions are practical and achievable.
Care planning software can simplify documentation, maintain consistency, and allow for tailored adjustments based on individual needs. Once a clear and collaborative plan is established, the focus shifts to selecting and carrying out the right nursing interventions.
sbb-itb-aa73634
Choosing and Applying Nursing Interventions
Selecting nursing interventions involves a careful and systematic process, guided by clinical judgment. This ensures that every action taken directly addresses the patient’s needs and enhances the quality of care provided.
Using the ADPIE Nursing Process
The ADPIE framework offers a clear structure for choosing appropriate interventions. This step-by-step process helps nurses align their actions with patient needs:
| Phase | Purpose | Key Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Assessment | Collect patient data | Record vitals, symptoms, and history |
| Diagnosis | Identify health issues | Determine specific nursing diagnoses |
| Planning | Create care plan | Set goals and choose interventions |
| Implementation | Carry out the plan | Perform and document interventions |
| Evaluation | Review outcomes | Assess results and make adjustments |
By following these steps, interventions are grounded in evidence and tailored to the patient’s care plan. For instance, if a patient is experiencing acute respiratory distress, immediate actions like oxygen therapy and proper positioning become priorities.
Applying Tanner’s Clinical Judgment Model
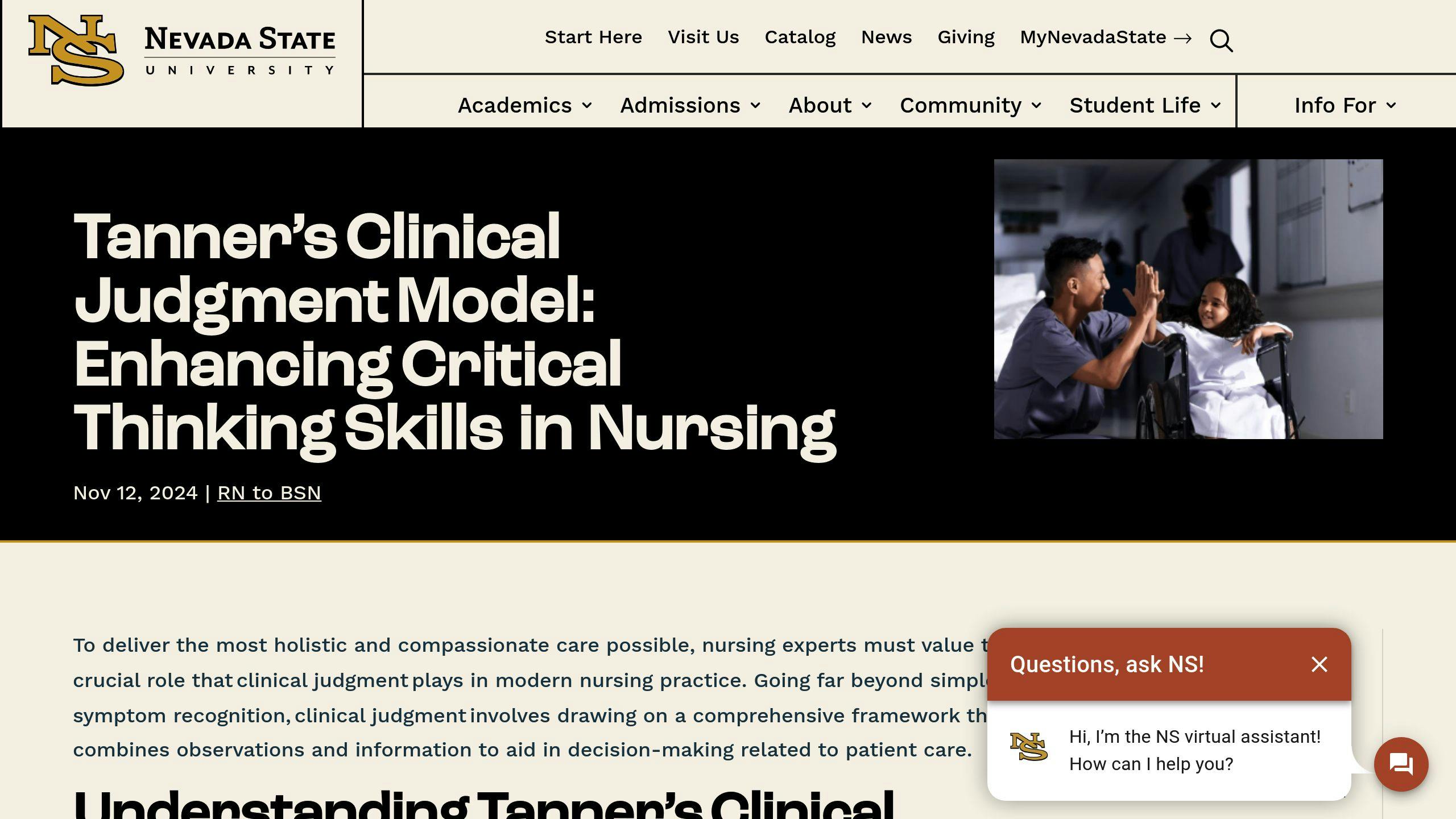
Tanner’s Clinical Judgment Model adds depth to decision-making, focusing on four key areas:
1. Noticing
Pay attention to subtle changes in the patient’s vitals, behavior, or symptoms that may indicate the need for specific interventions.
2. Interpreting
Analyze the observed data in the context of the patient’s overall condition. This step combines clinical expertise with the patient’s unique circumstances.
3. Responding
Choose and carry out suitable interventions based on the interpretation of the data, ensuring they align with evidence-based care and the patient’s individual needs.
4. Reflecting
Evaluate the outcomes of the interventions to refine future care decisions.
To make the most of these approaches, nurses should:
- Clearly communicate and document the reasons behind each intervention.
- Continuously monitor patient responses and adjust actions as needed.
- Take into account cultural and personal preferences to ensure patient-centered care.
Tips for Putting Interventions into Practice
Implementing nursing interventions effectively requires a mix of clinical knowledge, teamwork, and ongoing education. Here’s how to ensure your interventions align with patient needs while following workplace guidelines.
Working with Other Healthcare Professionals
Teamwork is at the heart of successful intervention implementation. According to the American Association of Critical-Care Nurses (AACN), collaboration across disciplines can significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce complications in critical care settings [1]. By combining diverse expertise, the care team can ensure that interventions are tailored to the patient’s specific needs.
Here are some ways to improve collaboration:
- Use clear communication tools like SBAR for handoffs and discussions.
- Actively engage in interdisciplinary rounds to share insights and intervention updates.
- Document interventions thoroughly to ensure smooth transitions between shifts.
Below is an overview of how different team members contribute to intervention success:
| Team Member | Role in Interventions | Collaboration Method |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Nurse | Leads assessment and implementation | Daily care planning and documentation |
| Physician | Provides medical direction | Regular rounds and care conferences |
| Specialist | Brings expertise for specific conditions | Consultations and treatment adjustments |
| Care Coordinator | Manages care across departments | Transition planning for continuity |
Using Educational Tools to Improve Skills
The Synergy Model highlights the importance of matching nurse skills with patient needs to ensure that interventions are both effective and patient-focused [1].
You can sharpen your intervention skills by reviewing complex cases, practicing through simulations, and working with scenario-based exercises. Standardized care plans can serve as helpful guides but should always be adapted to meet individual patient needs.
To enhance your skills:
- Stay Current with Evidence-Based Practices: Regularly review the latest research and participate in initiatives aimed at improving care quality.
- Engage in Quality Improvement Projects: Collaborate on projects designed to refine intervention strategies.
- Incorporate Feedback: Use patient satisfaction data and outcome measures to evaluate and adjust your interventions for better results.
Conclusion: Steps to Match Interventions to Patient Needs
Key Steps Overview
The Synergy Model offers a structured way to align patient needs with nursing skills through a series of interconnected steps [1]. These steps help nurses create care plans that are both effective and adaptable to the patient’s current condition.
| Step | Key Components |
|---|---|
| Assessment | Gathering detailed patient information and acuity measures |
| Care Planning | Setting priorities, involving families, and seeking input from other disciplines |
| Implementation | Applying the ADPIE process and using clinical judgment |
| Evaluation | Measuring outcomes and incorporating feedback |
Patient acuity-driven staffing helps improve care delivery and clinical results [2]. Following a clear, structured process ensures care is delivered effectively, but maintaining these skills requires ongoing professional development.
Continuous Skill Development
Growth in nursing comes from consistently building knowledge and refining skills. Resources like Nurse Cram support this by offering scenario-based practice and readiness exams, which enhance clinical judgment. Staying informed about updated guidelines and taking part in quality improvement initiatives helps ensure care remains evidence-based and impactful.
"The Synergy Model highlights how aligning patient needs with nurse skills leads to better outcomes and job satisfaction."
FAQs
Here’s a closer look at common questions about nursing interventions and how they align with patient care:
What are appropriate nursing interventions for any client?
Nursing interventions generally fall into three categories: routine interventions (like checking vital signs), dependent interventions (those requiring a physician’s order), and independent interventions (such as educating patients). The AACN Synergy Model emphasizes aligning a nurse’s skills with a patient’s specific needs to deliver effective care [1].
What are standard nursing interventions?
Standard interventions are designed to address patient needs based on their condition’s severity, ensuring resources are used wisely. These interventions follow evidence-based practices and are tailored to achieve specific care outcomes [2].
What are the 5 nursing interventions?
Here are five key examples of nursing interventions:
- Bedside care
- Administering medications
- Postpartum support
- Assisting with feeding
- Monitoring vital signs
What are some examples of nursing interventions?
Examples include providing physical care, educating patients, tracking vital signs, and coordinating care among providers. These actions should align with the patient’s medical needs and the established care plan [2].
"The AACN Synergy Model highlights how aligning patient needs with nurse skills leads to better outcomes and job satisfaction." [1]
Related posts
- 6 Clinical Judgment Skills for Analyzing Patient Data
- Prioritization and Delegation: Case Study Examples
- Clinical Judgment: Evaluating Interventions Explained
- Guide to Individualized Care Plans for NGN NCLEX

Mia is dedicated to helping nursing students and new graduates confidently prepare for the Next Generation NCLEX exam. With a focus on providing clear, actionable advice and support, Mia offers practical study tips, effective strategies, and encouragement to guide you through the complexities of nursing exams. Whether you need help mastering question formats, managing stress, or creating a personalized study plan, Mia is here to ensure you feel prepared and empowered every step of the way.

